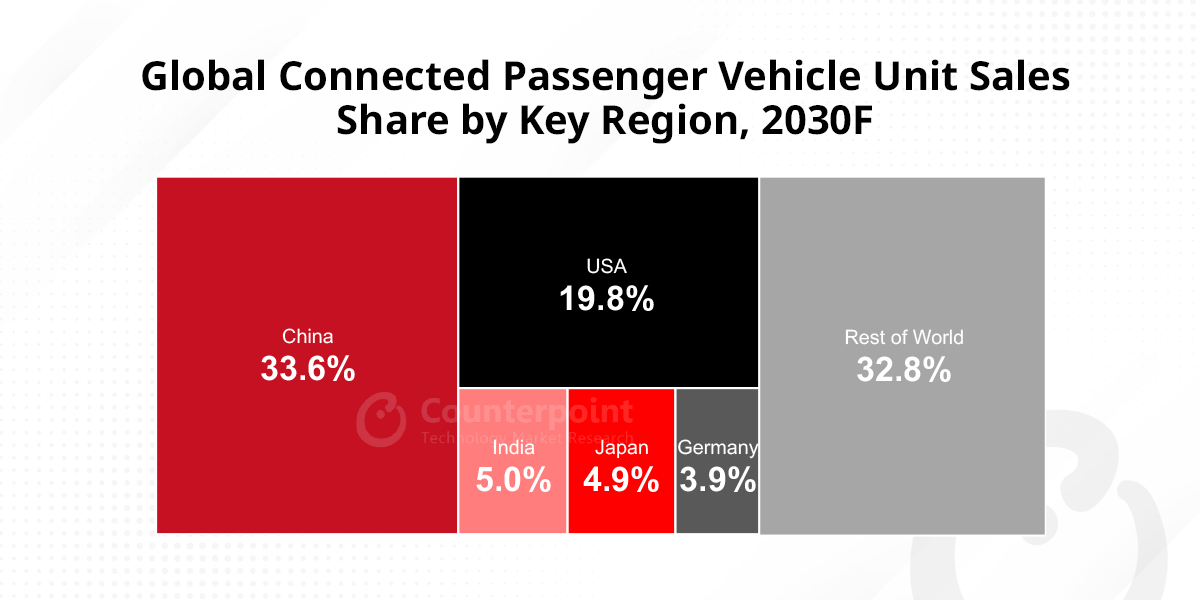
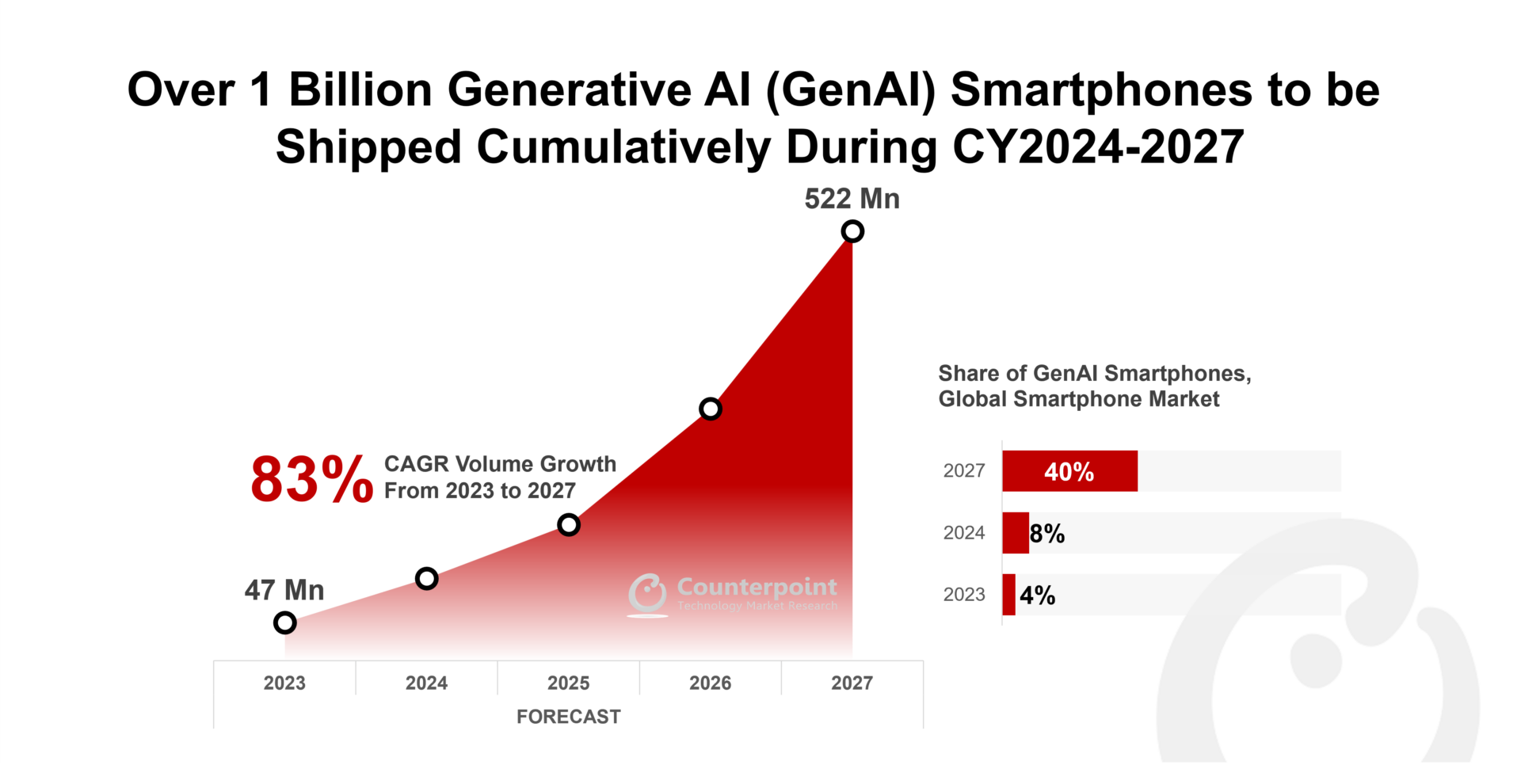
- Ericsson, Nokia, Samsung reported a decline in revenues in H1 2024.
- Ericsson incurred further impairment charges on account of Vonage, while Nokia is realigning its focus on the optical network front.
- Vendors are looking into different opportunities to monetize the 5G network.
- Uncertainty remains in the industry as operators are not able to monetize the investment, and vendors are pushing Operators to upgrade their networks.
Ericsson, Nokia, and Samsung each posted a decline in H1 2024 revenue as spending by network operators remained subdued due to macroeconomic challenges.
During H1 2024, Ericsson’s revenue fell 11% to $10.7 billion, while its counterpart Nokia’s revenue declined 21% to reach $9.9 billion. Samsung’s network division sales dropped 31% to reach $1.1 billion.
India, which was among the major customers in the 5G networks for Nordic vendors in 2023, experienced a major decline in CAPEX spending as major operators completed the initial phase of network deployment. Indian operators are now focusing on monetizing their investments rather than investing further in extending their networks.
During this period, Ericsson recorded an impairment cost of about $1.07 billion related to Vonage, adding to a previous impairment of around $2.95 billion stemming from challenges in the global CPaaS market caused by macroeconomic factors. Meanwhile, Nokia has sold its submarine network business and acquired Infinera to strengthen its focus on the optical network space, where it holds a leading position.
Ericsson
- The Network Infrastructure (NI) segment saw a 16% YoY decline during the period as operators reduced their spending in key markets, particularly India, following record investments in 2023. However, sales increased in North America due to Ericsson’s O-RAN-compliant network infrastructure deal with AT&T. The gross margin for this segment improved to 44.8% driven by new contract wins.
- The Cloud Software and Services (CSS) segment remained flat during the period, as operators cut back on managed services spending and was offset by an increase in core contracts. Additionally, Ericsson signed new IPR deals that helped mitigate the business decline. Ericsson remains a leading player in the 5G core market and holds the top position in the 5G SA core segment.
- Enterprise Wireless Solutions (EWS), which includes Cradlepoint, contributed to sales growth, while the Vonage Global Communications Platform (GCP) faced challenges due to reduced customer spending. The enterprise segment secured new deals in the private network space and made further advancements in the Global Network Platform for Network APIs, securing two new partnerships in Q2 2024. APIs are being reviewed as significant monetization avenues for operators.

Nokia
- The Network Infrastructure (NI) segment saw a revenue decline of 24% YoY in H1 2024 to reach $3.2 billion, due to the decrease in sales of optical and fixed networks. During the period, Nokia sold its submarine network business and acquired Infinera to increase its integration in the optical networks space. Nokia expects good traction during H2 2024 with flat revenue growth in 2024.
- Nokia’s Mobile Network (MN) business reported a revenue decline of 32% YoY to $3.8 billion, which was due to a reduction in spending by operators in India. Apart from that, the loss of AT&T as a major mobile network customer also impacted the segment. However, the margin improved to 42.9%.
- Cloud and Network Services (CNS) revenue declined by 16% YoY, while the operating margin declined by 4.1% due to the disposal of the Device Management and Service Management Platform business. On the core front, there has been a slowdown in operators’ transition to 5G SA, with most of them opting for Ericsson, which further dented Nokia’s CNS business.
- Nokia Technologies revenue increased 93% YoY to $1.2 billion as the company has renewed key license deals with OPPO and vivo. Revenue from Nokia’s enterprise customers decreased by 11% YoY to $1.04 billion as enterprises are reducing their spending on private wireless networks due to the global macroeconomic instability.

Samsung
- In H1 2024, revenue at Samsung’s mobile networks division declined 31% to $1.1 billion, as the brand is also facing the same global headwinds experienced by its Nordic counterparts.
- Samsung is among the leading players in the vRAN and Open RAN domains, although the Open RAN market is shifting from multi-vendor to single-vendor providers. Samsung remains optimistic about winning key contracts globally.
Key Takeaways
The market is facing challenges, with operators reducing their spending on the network infrastructure segment due to a lack of 5G monetization opportunities. Operators are continuously looking for avenues to realize returns on their investments as they are focusing on services like FWA, private networks, and network APIs.
The transition to 5G Standalone (SA) also slowed down during H1 2024 as operators claim that they do not see any business opportunities in deploying a dedicated 5G core. Although 5G FWA has come out as among the most promising applications of SA, operators are yet to find a way to monetize mMTC, URLLC, and enterprise customers.
Network vendors and operators are emphasizing network APIs, as they can be among the next major avenues for 5G monetization and are working with operators to identify multiple use cases. User Equipment Route Selection Policy (URSP) can also apply to network APIs for select applications.
5G is having a monetization problem and the advent of 5G-A is not likely to change the situation further. Network vendors will face further challenges, as operators are not likely to invest more in the infrastructure, unless they are incentivized. Although FWA is progressing rapidly, other use cases, including private networks are not executing as expected.
Ericsson and Nokia are re-aligning their strategies to focus on maintaining their bottom line. Ericsson is continuing to maintain its leadership in the RAN and core market and is increasing its presence in North America by taking market share from Nokia. Apart from that, it is increasing its presence in the enterprise segment through Cradlepoint and Global Communications through Vonage. Nokia, on the other hand, is strategizing its portfolio, as it has sold its submarine network business and acquired Infinera to increase its focus on the optical network market. Nokia has a strong presence in the fixed, optical, and private network markets and is looking to maintain its dominant position in the segment.
The market is facing challenges and network vendors are encouraging operators to upgrade their networks to 5G SA, 5G-Advanced, cloud-native core solutions, and multi-band massive MIMO radios to monetize their 5G investments. However, operators are reluctant because they do not see any immediate business opportunities and are adopting a “wait-and-see” attitude to further infrastructure investments. Apart from the increase in speed, operators have not really benefited from their 5G networks, and the enterprise segment is not seeing the need to increase their investment in upgrading their network solutions. However, the scenario could change going forward when newer and more cost-effective solutions become available, as the retail segment is not likely to be a major avenue for 5G monetization.